Islamic banking principles prohibit interest (riba) and promote risk-sharing. These principles align financial practices with Islamic law (Sharia).
Islamic banking focuses on ethical finance, aligning with Sharia law to ensure fairness and transparency. It avoids interest-based transactions, emphasizing profit-sharing and asset-backed financing. This banking system promotes risk-sharing between lender and borrower, fostering a cooperative financial environment. Contracts must be clear, and both parties should fully understand their rights and obligations.
Islamic banks also avoid investments in industries deemed harmful or unethical, such as alcohol or gambling. This ethical approach attracts individuals seeking socially responsible banking options. As Islamic finance grows globally, it offers a viable alternative to conventional banking, appealing to both Muslims and non-Muslims alike.
Related Article: Islamic Finance: Unlocking Ethical Investment Opportunities

Related Article: Zakat: Transforming Lives Through Compassionate Giving
Introduction To Islamic Banking
Islamic banking offers a unique approach to finance. It follows Sharia, or Islamic law. This system avoids interest and promotes ethical investment.
Core Concepts
Islamic banking stands on a few key principles:
- Prohibition of Riba (Interest): Charging interest is forbidden.
- Risk Sharing: Both profit and loss are shared between parties.
- Asset-Backed Financing: Transactions must be backed by real assets.
- Ethical Investments: Investments must support moral and ethical values.
- Avoidance of Uncertainty (Gharar): Contracts should be clear and certain.
Historical Background
Islamic banking has deep historical roots. Its principles are based on the Quran and Hadith.
Early Islamic societies practiced these principles. They engaged in trade and commerce without interest.
Modern Islamic banking began in the 1960s. It started in Egypt with the Mit Ghamr Savings Project.
Today, Islamic banking operates worldwide. It serves millions of people and businesses.
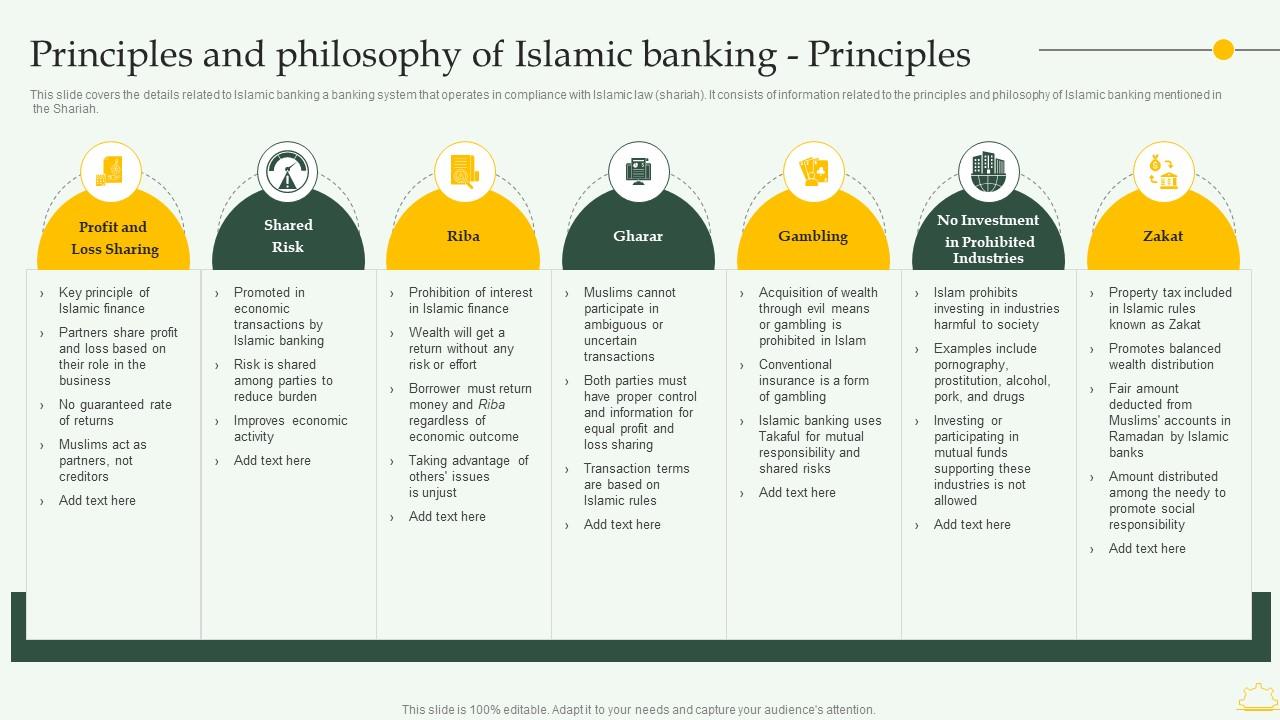
Principles Of Sharia Compliance
Islamic banking is governed by the principles of Sharia compliance. These principles ensure that financial transactions are conducted in a manner consistent with Islamic law. The key tenets include the prohibition of riba, risk-sharing, and ethical investments. Let’s explore these fundamental principles in detail.
Prohibition Of Riba
One of the core principles of Islamic banking is the prohibition of riba. Riba refers to any form of interest on loans. Islamic law forbids earning money through interest. This principle ensures that wealth is not generated through exploitative means. Instead, banks earn profit through equity participation.
In Islamic banking, both the lender and borrower share the risk. This aligns with the ethical standards of fairness and justice. The prohibition of riba promotes economic equality and prevents wealth accumulation by a few.
Risk Sharing
Another fundamental principle is risk sharing. This principle ensures that both parties involved in a financial transaction share the risks and rewards. Unlike conventional banking, where the burden of risk is on the borrower, Islamic banking distributes it equally.
Here are some key points about risk sharing:
- Promotes fairness and justice
- Encourages ethical investments
- Supports economic stability
Islamic banks use profit-sharing models like Mudarabah and Musharakah. These models ensure that profits and losses are shared equitably. This approach fosters a sense of partnership and trust.
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Prohibition of Riba | Interest-free financial transactions |
| Risk Sharing | Equitable distribution of risks and rewards |
Credit: www.slideteam.net
Ethical Investment Guidelines
Islamic Banking operates on a foundation of ethical investment principles. These principles ensure investments align with Islamic law and values. The goal is to promote fairness, transparency, and social responsibility. Below are key components of these guidelines.
Halal Investments
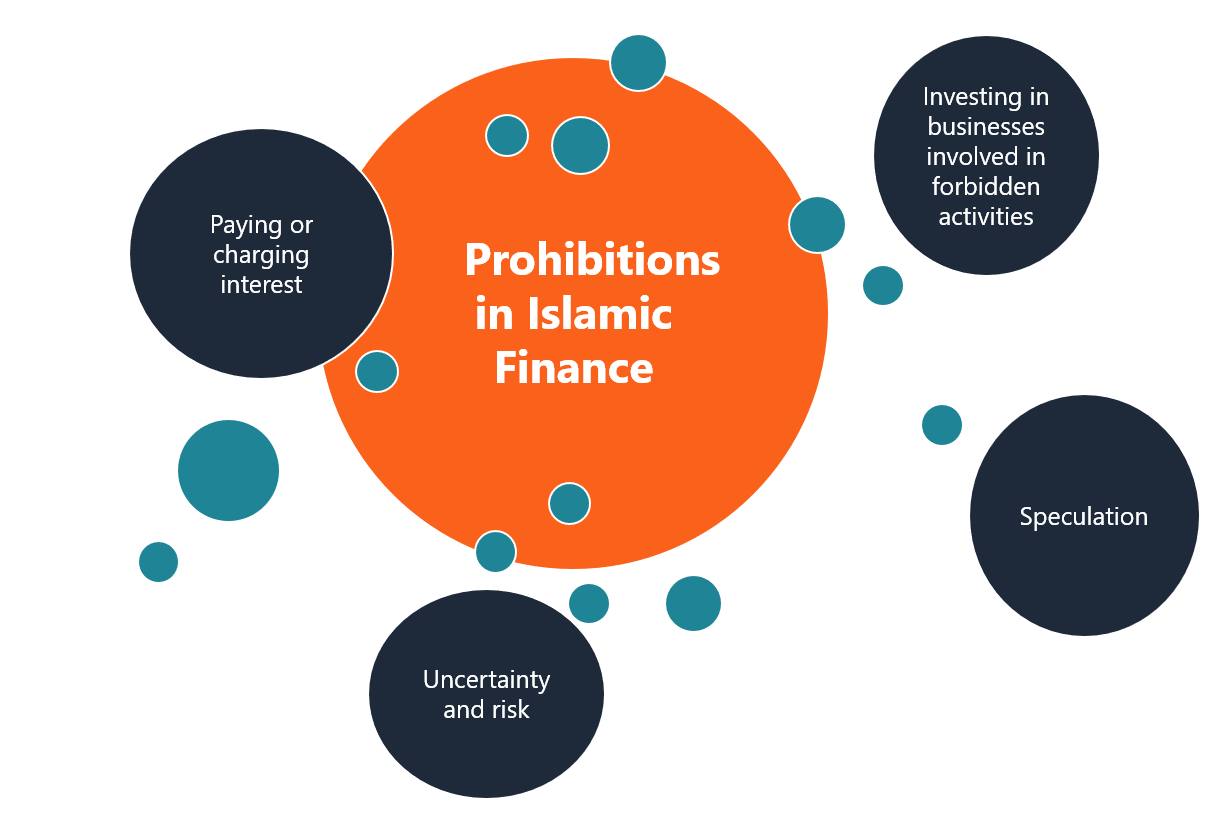
Investments in Islamic Banking must be Halal. This means they must be permissible under Islamic law. Here are some key points:
- Prohibition of Interest: Charging or paying interest (Riba) is not allowed.
- Avoidance of Unethical Businesses: Investments in alcohol, gambling, and pork products are forbidden.
- Risk-Sharing: Investments must involve risk and reward sharing between parties.
Table of Permissible vs. Non-Permissible Investments:
| Permissible (Halal) | Non-Permissible (Haram) |
|---|---|
| Real Estate | Gambling |
| Healthcare | Alcohol |
| Technology | Pork Products |
Social Responsibility
Islamic Banking also emphasizes Social Responsibility. Investments should benefit society. Here are key aspects:
- Charitable Giving: A portion of profits is donated to charity (Zakat).
- Environmental Sustainability: Investments should support eco-friendly practices.
- Community Development: Funds are directed towards projects that improve social welfare.
Socially responsible investments promote long-term societal benefits. They align financial goals with ethical values.
Islamic Financial Products
Islamic banking is unique. It follows Sharia law, which has specific rules for financial transactions. These rules create distinct products. Two key examples are Murabaha and Sukuk. Let’s explore these in detail.
Murabaha
Murabaha is a common Islamic financing technique. It involves a sale where the cost and profit margin are agreed upon by both parties. This type of transaction is similar to a cost-plus-profit sale.
Here’s how Murabaha works:
- The bank buys an asset.
- The bank sells the asset to the customer.
- The customer knows the cost and the profit margin.
- The customer pays over time.
Murabaha ensures transparency. Both parties know the exact costs involved. There are no hidden fees.
Sukuk
Sukuk is often called an Islamic bond. It represents ownership in a tangible asset, a project, or a business venture. Unlike traditional bonds, Sukuk holders get a share of profits from the asset.
Key features of Sukuk include:
- Asset-backed securities.
- Profit-sharing instead of interest.
- Compliance with Sharia law.
Sukuk offers a safe and ethical investment option for Muslims. It adheres strictly to Islamic principles.
Role Of Islamic Banks
Islamic banks play a vital role in the economy. They operate based on Sharia principles. These principles ensure fairness and transparency. Islamic banks do not charge interest. Instead, they engage in profit-sharing and trade-based activities.
Community Development
Islamic banks significantly contribute to community development. They invest in local projects. These projects include schools, hospitals, and roads. Such investments improve living standards. Islamic banks also support small businesses. This creates jobs and boosts the local economy.
Financial Inclusion
Islamic banks promote financial inclusion. They provide services to everyone, including the unbanked. Islamic banks offer microfinance options. These help people start small businesses. This encourages entrepreneurship in the community.
Islamic banks also offer Zakat accounts. Zakat is a form of charity. It helps the needy and supports community welfare. These accounts ensure that funds reach those in need. This strengthens social cohesion and reduces poverty.
| Role | Details |
|---|---|
| Community Development | Investing in infrastructure and small businesses |
| Financial Inclusion | Providing services to the unbanked and offering microfinance |

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Challenges And Opportunities
Islamic banking, rooted in Sharia principles, offers a unique financial system. It presents both challenges and opportunities on a global scale. Understanding these factors is crucial for stakeholders.
Global Market Integration
Integrating Islamic banking into the global market is complex. It requires harmonizing Sharia principles with international financial standards. Below are key points:
- Compliance with both Sharia and global financial regulations.
- Ensuring transparency in financial transactions.
- Developing competitive financial products within Sharia guidelines.
These challenges can also create opportunities. Islamic banks can tap into new markets. They can attract customers seeking ethical banking solutions.
Regulatory Issues
Regulatory issues pose significant challenges for Islamic banking. Different countries have varying regulations. This can affect the growth of Islamic finance. Consider the following:
| Country | Regulatory Body | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Malaysia | Bank Negara Malaysia | Ensuring Sharia compliance |
| Saudi Arabia | SAMA | Adapting to global standards |
| UK | FCA | Integrating with conventional banks |
Regulatory challenges can spur innovation. Islamic banks can develop new ways to comply with both Sharia and international norms.

Future Of Islamic Banking
The future of Islamic banking looks promising. The principles of Sharia-compliant finance continue to attract attention. With a focus on ethical practices, Islamic banking is poised for significant growth.
Technological Innovations
Technological innovations are transforming the Islamic banking sector. Digital platforms are making banking more accessible. Mobile banking apps are a game-changer. They offer convenience and efficiency.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain are also making an impact. AI helps banks analyze customer data. This leads to better service and customized products. Blockchain ensures secure and transparent transactions. It reduces fraud and increases trust.
| Technology | Impact |
|---|---|
| Mobile Banking Apps | Increased accessibility and convenience |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Enhanced data analysis and customer service |
| Blockchain | Secure and transparent transactions |
Sustainable Growth
Sustainable growth is a core focus for Islamic banking. Ethical investments are at the heart of this growth. Green financing is gaining momentum. Islamic banks invest in eco-friendly projects. These include renewable energy and sustainable agriculture.
Furthermore, Islamic banking promotes financial inclusion. It caters to underserved communities. Microfinance initiatives help small businesses thrive. By focusing on social welfare, Islamic banking ensures balanced growth.
- Green financing projects
- Investments in renewable energy
- Support for sustainable agriculture
- Financial inclusion efforts
- Microfinance for small businesses
Credit: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Conclusion
Islamic banking principles offer ethical and sustainable financial solutions. They align with Sharia law, promoting fairness and transparency. As awareness grows, more people explore these alternatives. Embracing these principles can lead to a more equitable financial system. Discover the benefits and consider Islamic banking for your financial needs.
Related Article: Zakat Al Fitr: A Complete Guide to Its Importance and Calculation




1 thought on “Islamic Banking Principles: Ethical Financial Solutions”